Development of critical thinking as a means of forming STEM competencies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31812/educdim.v55i0.3955Keywords:
STEM education, STEM competencies, critical thinking, competenceAbstract
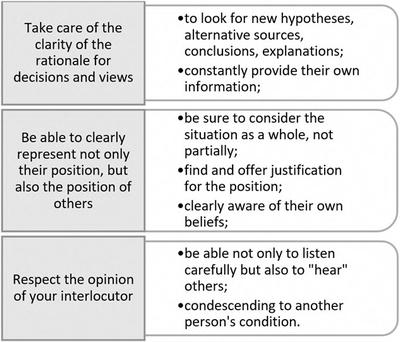
The article analyzes the scientific literature in order to determine different approaches to the interpretation of the concept of “critical thinking”, describes its components, discusses the basic concepts, functions of critical thinking in teaching. Critical thinking is presented as one of the main competences of STEM education. The conditions for the development of critical thinking in the process of STEM-learning are determined. Methodical problems are solved, which should help students to develop STEM competences based on the development of their critical thinking.
Downloads
References
Dewey, J.: Method in science teaching. General Science Quarterly 1 (1), 3–9 (1916) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.3730010101
Lipman, M.: Thinking in Education. Cambridge University Press, New York (1991)
Clusters, D.: What is critical thinking. Pervoe sentybrya 29 3 (2002)
Paul, R., Elder, L.: A guide for educators to critical thinking competency standards. Foundation for Critical Thinking, Dillon Beach (2007)
Pintrich, P. R.: Chapter 14 - The Role of Goal Orientation in Self-Regulated Learning. In: Boekaerts, M., Pintrich P. R., Zeidner, M. (eds.) Handbook of Self-Regulation, pp. 452–502. Academic Press, Cambridge (2000). doi: 10.1016/B978-012109890-2/50043-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-012109890-2/50043-3
Sternberg, R. J., Halpern, D. F. (eds.): Critical Thinking in Psychology, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York (2000)
Sternberg, R. J.: Critical Thinking: Its Nature, Measurement, and Improvement. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED272882.pdf (1986)
Kallet, M.: Think Smarter: Critical Thinking to Improve Problem-Solving and Decision-Making Skills. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2014)
Kozachenko, N.: Critical thinking: the limiting approaches and optimal ways. Actual Problems of Mind. Philosophy Journal (18), 165–178 (2017). doi: 10.31812/apd.v18i1.24 DOI: https://doi.org/10.31812/apd.v18i1.24
Honcharenko, S. U.: Pedahohichni doslidzhennia. Metodolohichni porady molodym naukovtsiam (Pedagogical research. Methodological advice for young scientists). Vinnytsia, Kyiv (2008)
Mikhailov, F. T.: Filosofiia obrazovaniia: sostoianie, problemy i perspektivy. Materialy zaochnogo kruglogo stola (Philosophy of education: state, problems and prospects. Materials of the correspondence round table). Voprosy filosofii 11 (1995)
Maksimenko, S. D.: Myslennia (Thinking). In: Zaichuk, V., Klimenko, V., Solovienko, V. (eds.) Zahalna psyhologiia (General psychology) (2000)
Ennis, R. H.: Critical Thinking and Subject Specificity: Clarification and Needed Research. Educational Researcher 18 (3), 4–10 (1989). doi: 10.2307/1174885 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X018003004
Glaser, E. M.: An experiment in the development of critical thinking. Teachers College, Columbia University, New York (1941)
Mason, M. (ed.): Critical Thinking and Learning. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken (2008) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444306774
McPeck, J. E.: Critical Thinking and Education. Martin Robertson, Oxford (1981)
Draft concept of STEM education in Ukraine. http://mk-kor.at.ua/STEM/STEM_2017.pdf (2017). Accessed 29 Nov 2019
Tiaglo, A. V., Voropai, T. S.: Kriticheskoe myshlenie: Problema mirovogo obrazovaniia XXI veka (Critical Thinking: The Problem of World Education in the XXI Century). University of Internal Affairs, Kharkov (1999)
Terno, S. O.: Teoriia rozvytku krytychnoho myslennia (na prykladi navchannia istorii) (Theory of the development of critical thinking (on the example of teaching history)). Zaporizkyi natsionalnyi universytet, Zaporizhzhia (2011)
Downloads
Submitted
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 Olha Pylypenko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Accepted 2020-03-24
Published 2020-12-10








